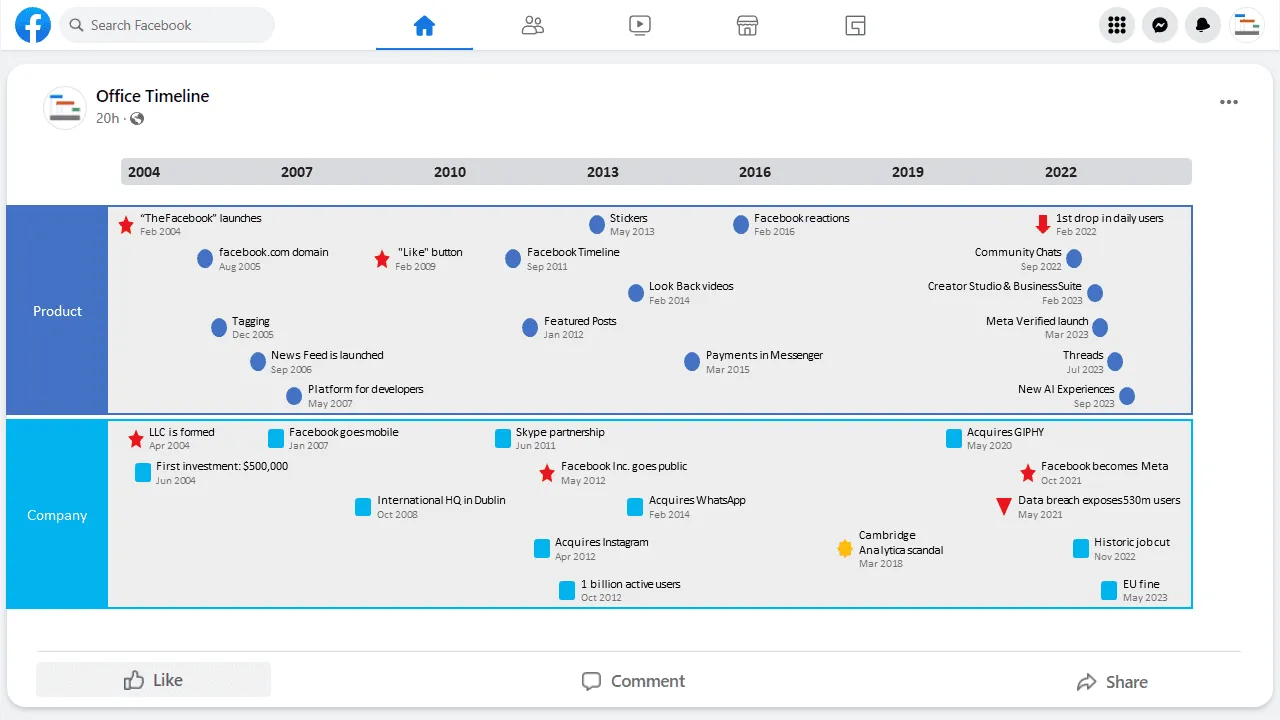
Facebook history timeline
The Facebook history timeline illustrates important events in the narrative of the social networking platform.
Last updated on February 6, 2024
On February 4, 2004, Mark Zuckerberg launched a social website called “TheFacebook” (currently known as “Facebook“) from his dorm room at Harvard. Soon, what started as a private network for college students became a worldwide phenomenon, everyone from teens to grandmothers using it to catch up with friends and get their news. For those interested in the history of Facebook rather than the news on Facebook, here’s a timeline of the milestones that helped shape the social media giant we know today.
The Facebook history timeline illustrates important events, achievements, and releases in the narrative of the social networking platform, from the day the service was launched to the present day. Below the timeline, you will also find a series of frequently asked questions regarding the company and its evolution throughout the years.
Note: some of the events described below are hidden on the visual timeline for brevity purposes. However, you can unhide them by following the step-by-step instructions in our support article.
The history of Facebook: a timeline
- 2004, February 4: “TheFacebook” launches
- 2004, April 13: LLC is formed
- 2004, June: First official investment
- 2004, September: ConnectU sues Facebook
- 2005, August: The company acquires the facebook.com domain and drops the “The” in its name
- 2005, December: Introduces tagging
- 2006: News Feed is launched
- 2007, January: Facebook goes mobile
- 2007, May: Launches Facebook Platform for developers
- 2007, November: Launches Facebook Beacon, a targeted ad system that published the users’ activities on external sites without permission, creating significant privacy concerns and resulting in a class-action lawsuit.
- 2008, June: Settles dispute with ConnectU
- 2008, October: International headquarters in Dublin
- 2009, February: The “Like” button is introduced
- 2009, November: Beacon is shut down
- 2011, June: Facebook partners with Skype to add video chat
- 2011, November: Facebook Timeline is introduced
- 2012, January: Featured Posts start showing in the News Feed
- 2012, April: Facebook acquires Instagram
- 2012, May: Facebook goes public
- 2012, October: The social media platform reaches 1 billion active users, an important milestone in Facebook’s history timeline
- 2013, May: Stickers are launched
- 2013, August: Launches Internet.org
- 2014, February: Acquires WhatsApp
- 2014, February: Look Back videos are introduced
- 2014, October: Creates custom Tor link
- 2015, March: Peer-to-peer payments in Messenger
- 2015, May: Announces support for GIFs
- 2016, February: Facebook reactions are launched
- 2016, June: Secret soccer game in Messenger
- 2017, April: Announces Facebook Spaces
- 2017, October: Acquires social media app tbh
- 2018, March: The Cambridge Analytica data scandal starts, probably the biggest in the history of Facebook
- 2020, May: Purchases GIPHY
- 2020, June: Launches Dark Mode for mobile
- 2021, May: Data breach exposes 530m users
- 2021, October: Facebook Inc. renamed as Meta Platforms Inc.
- 2021, November: Shutdown of face recognition
- 2022, February: Daily active users drop for the first time
- 2022, March: Eases rules to allow violent speech against ‘Russian invaders’
- 2022, May 9: Meta’s first store
- 2022, August 27: Cambridge Analytica settlement
- 2022, September 14: Community Chats
- 2022, October 11: NBCUniversal and Microsoft
- 2022, October 25: Quest Pro
- 2022, November: Historic job cut
- 2023, February 8: Creator Studio & Business Suite
- 2023, February 24: LLaMA
- 2023, February 27: Shift toGenerative AI
- 2023, March 17: Meta Verified launch
- 2023, May 4: AR ads
- 2023, May 22: EU fine
- 2023, June 1: Quest 3
- 2023, July 5: Threads
- 2023, September 23: Llama 2
- 2023, September 27: New AI Experiences
- 2023, October 17: Ray-Ban Meta Smart Glasses
- 2023, November 7: Lantern
- 2023, November 16: Emu Video and Emu Edit
- 2024, January 18: Announces AGI
Facebook timeline history: a detailed look
The timeline shows all major events, milestones, and releases in the story of the platform, from the day it first came online to today. Now, let’s go step by step over the details of each milestone in order to get a better idea about how the company has changed over time.
2004, February 4: “TheFacebook” launches
Mark Zuckerberg launched the early version of Facebook, that had a restricted audience and limited features.
2004, April 13: LLC is formed
On April 13, 2004, Facebook passed a milestone by formally establishing itself as a limited liability company (LLC). This legal structure was very important for giving the company a framework and ensuring legal clarity in its early stages of growth.
2004, June: First official investment
In June 2004, Facebook raised its first venture capital in the form of $500,000 from investor Peter Thiel. This funding, an important support at the right time, was a major factor in Facebook’s early expansion and pioneering of new features which both paved the way for its future growth into a global social media giant.
2004, September: ConnectU sues Facebook
In September 2004, ConnectU sued Facebook, claiming Mark Zuckerberg had improperly used source code and design concepts of ConnectU. The lawsuit alleged theft of intellectual property and breach of contractual obligations, marking the beginning of a legal dispute between two social networking rivals. ConnectU LLC alleges he not only stole their idea (called Harvard Connection), but also eroded it through deception.
2005, August: facebook.com domain
The company acquires the facebook.com domain and drops the “The” in its name.
2005, December: Introduces tagging
In December 2005, Facebook added a tagging feature, allowing users to identify and mention friends in pictures, posts, and comments. This enriched the social interaction of the platform and user engagement.
2006: News Feed is launched
Facebook launched the News Feed feature, providing users with a real-time, personalized stream of updates on friends’ activities and events, a considerable change to both content delivery and overall user experience on the platform.
2007, January: Facebook goes mobile
Facebook continued its growth in the first month of 2007, when mobile access was launched. Mobile users could now access the platform directly from their cell phones, further enhancing the image and convenience of social networking with technology.
2007, May: Launches Facebook Platform for developers
In May 2007, Facebook unveiled the Facebook Platform, which was designed to provide developers with tools to create third-party applications, games, and features within the Facebook ecosystem. The move opened up new opportunities for innovation.
2007, November: Facebook Beacon
Launches Facebook Beacon, a targeted ad system that published the users’ activities on external sites without permission, creating significant privacy concerns and resulting in a class-action lawsuit.
2008, June: Settles dispute with ConnectU
In June 2008, Facebook settled its legal dispute with ConnectU, resolving the long-standing litigation that originated from ConnectU’s allegations of intellectual property theft and breach of contract against Facebook. The settlement marked the conclusion of the legal conflict between the two social networking platforms.
2008, October 2: International headquarters in Dublin
On October 2, 2008, Facebook established its international headquarters in Dublin, Ireland, signaling the company’s global expansion and commitment to serving its growing user base outside the United States.
2009, February: The “Like” button is introduced
In February 2009, Facebook introduced the “Like” button, allowing users to express their approval or appreciation for posts and comments with a simple click. The “Like” button quickly became a hallmark of Facebook, reshaping user interaction with other people and the content on this site.
November 2009: Beacon is shut down
In November 2009, Facebook discontinued the Beacon functionality, which had drawn privacy concerns. Beacon came with an ad system broadcasting the activities of users on third-party websites to their friends in Facebook. Facebook’s decision to end Beacon showed how the system was responding to user privacy complaints and critiques about it.
2011, June: Facebook partners with Skype to add video chat
In June 2011, Facebook and Skype announced a partnership to enable video chat on the platform so that people could carry on real-time video conversations with their friends directly on Facebook.
2011, November : Facebook Timeline is born
Facebook Timeline was introduced in November 2011. The feature organized profile pages in chronological order, allowing users to display their most important life events, all accompanied by photos and activities. This structured way to show events revolutionized user profiles in a capital way, offering a new and more story-like approach to presenting personal content on the site.
2012, January: Featured Posts start showing in the News Feed
In January 2012, Facebook implemented Featured Posts in the News Feed. With this function, users had greater control over the visibility and prominence of particular posts when they were shared among friends.
2012, April: Facebook acquires Instagram
Facebook acquires Instagram, a highly popular photo app, for nearly $1 billion. This strategic acquisition has extended Facebook’s reach in the mobile and visual content space.
2012, April: Facebook acquires Instagram
In April 2012, Facebook acquires Instagram, a photo-sharing app that had quickly scaled to prominence. This acquisition strengthened the company’s role in both mobile and visual content.
2012, May: Facebook goes public
In May of 2012, Facebook held its initial public offering and launched its stock onto the market. The IPO was a major turning point for the company, marking its transition from a private entity to a public one. It drew widespread attention in the financial sector and helped position the company in the corporate world.
2012, October: 1 billion active users
The social media platform reaches 1 billion active users, an important milestone in Facebook’s history timeline.
2013, May: Stickers are launched
Stickers were first included in Facebook’s site in May 2013, giving users an appealing and colorful way to change the nature of their conversations by using images and animations in their messages and comments. This made communication on the platform more fun.
2013, August: Launches Internet.org
Facebook introduced Internet.org in August 2013, an effort that aimed to get Internet access to the under privileged and promote worldwide connectivity. The concept combined Facebook’s goal of bridging the digital divide with increasing Internet penetration globally.
2014, February: Acquires WhatsApp
Facebook acquires a leading messaging app, WhatsApp for a substantial sum. In doing so, the strategic motivation was to increase Facebook’s share in mobile messaging and expand its range of social communication products.
2014, February: Look Back videos are introduced
Facebook introduced Look Back videos, a feature that enables users to create personal video compilations of their memories on the platform. This feature represented a creative and nostalgic addition to Facebook’s products, which also increased user involvement and interactions.
2014, October: Creates custom Tor link
In October 2014, Facebook introduced a tailored Tor link that users could use to access the platform via the Tor anonymity network. In doing so, the company aimed to improve user privacy and the security of those who used the site anonymously.
2015, March: Peer-to-peer payments in Messenger
Facebook added peer-to-peer payment capability to Messenger, allowing users to get and send money directly through its messaging function. This expanded Messenger’s utility beyond conversation.
2015, May: Announces support for GIFs
Facebook first lets users embed GIFs into their comments, adding live-action effects to human interaction. This addition brought a lively element to the already-existing comments system on the platform.
2016, February: Facebook reactions are launched
Facebook introduces Reactions, expanding on the traditional “Like” button with a more nuanced set of emotions such as “Love,” “Ha-ha,” “Wow,” “Sad,” and “Angry.” The feature enabled users to express their sentiments about posts in nuanced ways.
2016, June: Secret soccer game in Messenger
Facebook introduces a secret soccer game within Messenger allowing users to engage in a fun, hidden gaming experience.
2017, April: Announces Facebook Spaces
Facebook Spaces, a virtual reality experience, was a new platform where users could interact with each other in a shared virtual environment, enjoying space or time together, but never leaving home. The company’s entered into the domain of virtual reality and social interactions.
2017, October: Acquires social media app tbh
In October 2017, Facebook takes over a popular social media app named tbh. It features positive and anonymous polling features. This was a step in Facebook’s activities to test new, modern methods for engaging users in the younger demographics.
2018, March: The Cambridge Analytica data scandal
The Cambridge Analytica data scandal starts, probably the biggest in the history of Facebook. The personal data of millions of users was improperly accessed and used for political purposes. This incident raised concerns about user privacy and started a broader conversation about data security on social media platforms.
2020, May: Purchases GIPHY
Adopted by Facebook in May 2020, GIPHY was an online platform that allows people to create and share animated GIFs. The goal of GIPHY’s integration was to make the visuals at Facebook’s properties more fun and interesting.
2020, June: Launches Dark Mode for mobile
In June 2020, Facebook adds Dark Mode for its mobile applications, offering users an alternative interface theme in darker colors. This feature was meant to bring a better viewing experience to night reading and offered different display modes as they have been required by users.
2021, May: Data breach exposes 530m users
In May 2021, a significant data breach exposes the personal information of approximately 530 million Facebook users. It forced Facebook to publicly address user privacy and security concerns and take steps to improve information security and implement measures to enhance data protection.
2021, October: Facebook Inc. renamed Meta Platforms Inc.
In October 2021, Facebook Inc. undergoes a significant rebranding and became Meta Platforms Inc. This name change reflected the company’s expanded focus on the metaverse. It represented the company’s new and higher ambition, looking beyond social media like a vision of a world where it is part platform and part real.
2021, November: Shutdown of face recognition
In November 2021, Facebook declares face recognition out of service. This choice showed that the company changed how it handles user privacy. It aimed to address worries about using facial recognition technology and how it affects keeping data safe.
2022, February: Daily active users drop for the first time
Facebook sees a noticeable decline in daily active users in Feb. 2022, the first time such a decline was registered. What raised the question of this event was whether there is less user engagement on Facebook and what other factors might be affecting user behavior.
2022, March: Eases rules to allow violent speech against ‘Russian invaders’
Facebook makes a controversial decision to relax its rules for content moderation allowing the expression of violent speech against ‘Russian invaders’ in the context of the war in Ukraine. This triggered debates on the nature of content moderation policies and how the platform should handle them.
2022, May 9: Meta opens its first store
Meta Platforms Inc. opens its first physical store in Burlingame, California. The store was Metaverse-themed, featuring three products: the Quest Two VR headset, Ray Ban Stories “smart glasses,” and Portal video calling device, offering consumers VR hands-on experience. The company is considering potential expansions based on insights gained from this store.
2022, August 27: Cambridge Analytica settlement
Meta reached a settlement in the lawsuit accusing Facebook of unlawfully sharing user data with the UK data analysis firm Cambridge Analytica. The data was reportedly used in political campaigns during the events of 2016 including Donald Trump’s presidential election and the UK’s EU referendum.
2022, September 14: Community Chats
Facebook launches a new Community Chats feature. It combines Messenger and Facebook Groups. This makes it possible to create real-time chat, voice, and video channels right there in the Messenger app. Admins can organize discussions by adding categories and adding new opportunities for user engagement and growth within Facebook and Messenger Groups.
2022, October 11: Partnerships with NBCUniversal and Microsoft
Meta’s partnerships with NBCUniversal and Microsoft aim to mark a new era for Quest VR. Meta teams up with NBCUniversal to bring Peacock streaming along, with popular content, seeking to attract more users. Microsoft is improving Quest VR by Teams, Windows apps, and Xbox Cloud Gaming, aiming to develop a world in which people can communicate, work together, and use Microsoft 365 productivity tools from their Quest devices. Xbox Cloud Gaming will also beam games to a 2D VR on Quest.
2022, October 25: Quest Pro
The Quest Pro, Meta’s VR headset is launched (going from $1,499.99 at launch to $999.99 towards the end of the year) ass a multitasking tool, not meant for the mass market. Its main appeal was its full-color passthrough, with four cameras outside to give a “mixed reality” experience.
2022, November: Historic job cut
Meta lays off 11,000 employees, marking its largest workforce reduction, representing approximately 13% of its total staff.
2023, February 8: Creator Studio & Business Suite
Creator Studio merged with Business Suite. A new pop-up replacing the familiar Creator Studio dashboard redirects users to the updated Meta Business Suite. The Business Suite introduces enhanced features like insights, Ads Manager, and monetization tools.
2023, February 24: LLaMA
Meta has introduced LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI), a 65-billion-parameter foundational large language model. It is designed to aid researchers in the AI subfield. By presenting LLaMA, Meta seeks to democratize access to such models, providing opportunities for researchers without substantial infrastructure access to engage with this field.
2023, February 27: Shift from metaverse to generative AI
Meta announces the creation of a new group focused on generative AI and led by ex-Apple executive Ahmed Al-Dahle. The group aims to offer “creative and expressive tools”, including generative AI-powered chat experiences in WhatsApp and Messenger. Meta sustained losses of $13.7B through October 2022 on metaverse development, attributing the losses to low user engagement.
2023, March 17: Meta Verified launches
The subscription service Meta Verified, present on Facebook and Instagram, is live in the US. Later same year it would be launched to most markets globally. Meta Verified aims to assist everyone with a blue check in enjoying the services, providing creators with verification through a government ID, account safety check and proactive account protection, access to direct account support and exclusive features.
2023, May 4: Augmented Reality (AR) ads
Meta introduces augmented reality to Reels Ads and Facebook Stories which brings a new dimension in user experience. This move enhances marketing with immersive experiences and AR filters for a more engaging audience, including Gen Z users. Brands can now collaborate with third-party measurement partners for Reels Ads campaigns.
2023, May 22: Fined for privacy breach
Meta was penalized $1.3 billion by the European Union for breaching its data privacy regulations by transferring user data from Europe to the US.
2023, June 1: Launches Quest 3 VR headset
The Quest 3 improvements: a lighter, slimmer design, a Qualcomm chip providing double graphics power, buyers can upgrade to 72-bit FPU silicon and additional storage options. The 128GB version was priced at $499.99.
2023, July 5: Launches Threads
Meta has entered competition with Twitter by introducing the Threads app. The app, focusing on real-time conversations, has garnered 30 million sign-ups, creating a welcoming public space to connect like-minded individuals.
September 23, 2023: Launches Llama 2
LLama 2 includes starting code for pretrained and fine-tuned language models (Llama Chat, Code Llama) with parameters ranging from 7B to 70B. Trained on 2 trillion tokens, Llama 2 has double the context length of Llama 1. It outperforms other open-source language models on benchmarks including reasoning, coding, proficiency, and knowledge tests.
2023, September 27: New AI Experiences
Facebook announces new AI Experiences across apps and devices in September 2023. In a nutshell: Meta releases AI stickers and editing tools for image cooperation; Meta AI, a conversational assistant, is in beta on WhatsApp, Messenger, and Instagram, expanding to smart glasses and Quest 3; a total of 28 new AI betas are launched, including those played by cultural celebrities; meta plans to offer AIs to businesses and creators, also adding an AI studio so companies can customize and build their own Ais.
2023, October 17: Launches Ray-Ban Meta Smart Glasses
Meta and Ray-Ban launched Ray-Ban Meta Smart Glasses with upgraded cameras, a personal audio system, livestreaming capability and their own security system to address privacy concerns. The 32GB version offers 12-megapixel photos and 1080p videos and is equipped with five microphones. The batteries are Qualcomm’s Snapdragon AR1 Gen 1, guaranteed to last 4 to 6 hours on active service.
2023, November 7: Lantern
The Tech Coalition launches Lantern, the first child safety cross-platform sharing program. The Tech Coalition, an alliance of global tech companies, includes Meta, Google, Discord and others, with the aim to fight online child exploitation.
2023, November 16: Emu Video and Emu Edit
The EMU Meta AI is launched in September 2023. Now, Meta introduces Emu Video and Emu Edit. Emu Video employs the Emu model in a two-step process: first, it generates images from a given text prompt and then produces videos conditioned on the text and the generated image. Emu Edit can implement detailed editing instructions when creating images and performing editing duties with excellent results in various image editing tasks.
2024, January 18: Announces AGI
Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg announces plans to develop open-source artificial general intelligence (AGI) by bringing together FAIR and GenAI teams. The goal is to build full general intelligence, capable of performing tasks requiring human-like cognitive abilities and make it widely accessible through responsible open sourcing. Zuckerberg envisions advancing AI in reasoning, planning, coding, memory, and cognitive abilities for various applications.
FAQ about Facebook
Still thirsty for info after reading the Facebook history timeline? Then let’s go with the flow and discover the answers to the most common questions about the social media giant.
Officially, Facebook was launched on February 4, 2004, by Mark Zuckerberg and fellow Harvard students Eduardo Saverin, Dustin Moskovitz, Andrew McCollum, and Chris Hughes. Back then, the site was intended as a social media platform for Harvard students exclusively. However, the story of how it started is a little more complicated than that and has sparked quite a bit of controversy.
It all started in 2003, when Zuckerberg created FaceMash, a platform that allowed users to compare photos of colleagues and decide who was “hotter”. FaceMash was problematic and short-lived, yet surprisingly popular, leading Zuckerberg to see the potential of a campus-wide social network. And so, the next year, he launched the “TheFacebook”, which became an instant hit.
The problem? Well, just a week after the launch, Zuckerberg was accused by three Harvard seniors that the idea was stolen from them. This resulted in a lawsuit, which settled in 2008 with the each of the accusers getting 1.2 million shares in the company.
Mark Zuckerberg created Facebook to help Harvard students connect with one another. Back then, there weren’t any universal online face books at the university. Sororities and fraternities each had their own individual directories, and there were paper sheets with student and staff profiles distributed to freshmen, but there was no centralized platform. This is what Zuckerberg tried to do with Facebook: gather all that information in one place so that all students at Harvard can learn about each other and communicate with one another.
Facebook was an instant hit. Within the first month after its official launch in February 2004, over half of Harvard’s undergrad students were already registered on the platform. In March that year, the site expanded to Yale, Columbia and Stanford too, and it was gradually adopted by most universities in the US and Canada. In 2005, Facebook opened to high school students too, and in 2006 it was made available to the general public.
By the end of 2005, the platform already had 6 million users, and it continued to grow exponentially over the years. As you can see on the Facebook history timeline, the site reached a whopping 1 billion active users in October 2012.
When launched officially in 2004, the social networking site was originally called “TheFacebook”. The company gave up the “The” from its name after purchasing the facebook.com domain in August 2005, for which it paid $200,000. Now, if you consider FaceMash to be a first version of Facebook (we’re talking about the “Hot or Not” social site that inspired Zuckerberg to build Facebook), you could say “FaceMash” was the original name of the renowned platform.
Facebook, Inc. (now Meta Platforms, Inc.) IPOed in 2012, so it is publicly owned. However, co-founder and chairman Mark Zuckerberg is the largest shareholder, owning 29.3% of the company, as well as the only CEO throughout the history of Facebook. Therefore, Zuckerberg is largely seen as the owner of the enterprise.
Unsurprisingly, Facebook’s first user was the founder himself, Mark Zuckerberg. He had the first official account ever created on Facebook, with ID #4. Accounts #1 to #3 were tests made by Zuckerberg, which he deleted afterwards. Next after him were co-founders Chris Hughes and Dustin Moskovitz. The first non-founder Facebook user was Arie Hasit, a friend of the founders who wasn’t involved in the project as he wasn’t interested in computer science.
Well, it depends who you ask. If you ask Zuckerberg, the answer will be no. But Facebook has had its fair share of scandals and controversies throughout its history, and one of the first is the accusation that Mark Zuckerberg stole the idea for Facebook from ConnectU (originally called HarvardConnection.com), which involved three Harvard seniors who were building a – wait for it – social network for Harvard.
The three students – Divya Narendra and brothers Tyler & Cameron Winklevoss – accused Zuckerberg of pretending to help them build the social network they envisioned, but instead stealing their idea to create Facebook. After a 4-year-long legal battle, Facebook ended up paying each of the three accusers 1.2 million in shares. Since the lawsuit ended in a settlement that involved paying quite a big amount to the accusers, one might draw the conclusion that there may be some legitimacy to the claims.
As you can see on the Facebook history timeline, Facebook (the company, not the app) changed its name to Meta Platforms in October 2021. But why the rename? Well, quite a lot of voices said it happened in an attempt to shake off the scandals the company has had been involved in the last years, including spreading misinformation, data leaks, and others. However, CEO Mark Zuckerberg stated that Facebook changed its name primarily because the “Meta” name was more closely aligned with what the company was working toward, namely the “metaverse”, an online virtual space that would unify multiple disparate digital worlds.
As of July 2022, Mark Zuckerberg’s net worth is $63 billion according to Bloomberg’s Billionaires Index. The Facebook founder has lost over 50% of his wealth in 2022. Still, he remains one of the richest people in the world, currently ranking 17th.
It’s estimated that Facebook (Meta Platforms) owns over 90 companies, many of which are hidden to the public, so it would be quite difficult to list them all. However, here are a few of the top companies owned by the social media giant:
• Instagram
• Giphy
• WhatsApp
• Oculus VR
• Onavo
• Tbh
• ConnectU – Yes, you read that right. This is the exact same company that’s known in the history of Facebook as the one that accused Zuckerberg of stealing the idea for the social networking platform. As a result of the lawsuit settled in 2008, besides other payments Facebook made towards the accusers, it also bought ConnectU as part of the settlement.
• Atlas Solutions
• LiveRail
• RedKix
• CTRL-Labs
• Beluga
• Spool
• FriendFeed
Yes, Facebook does own Instagram, widely abbreviated online as IG. The Facebook history timeline shows that the company acquired IG in 2012. They paid $1 billion for IG, a shocking sum at the time. According to email exchanges between Zuckerberg and former CFO David Ebersman made public by the US House antitrust committee, the company wanted to purchase Instagram to avoid competition. They saw IG as a potential threat to the social network, which could take business away from Facebook. Other sources say that the real reason Facebook became the owner of Instagram was to fend off competition from Google+ and Twitter.
No, Facebook does no own TikTok. The popular video hosting service is owned by ByteDance, a Chinese multinational IT corporation headquartered in Beijing. Interestingly enough, while it does not own the video sharing app, Facebook has an account on TikTok. The account seems to have been set up in March, 2022, and it is verified and confirmed to be legitimate.
No, never in the history of Facebook has the social networking platform been owned by Google. Facebook is a publicly owned company, with its largest three shareholders being Mark Zuckerberg, Jim Breyer & Accel Partners, and co-founder Dustin Moskovitz.
Facebook keeps repeating in its privacy policies and public statements that it does not sell your data to third parties. And if we were to take that literally, it’s absolutely true. The company indeed doesn’t sell your data – not directly. What it sells instead is targeted advertising, allowing third parties to use the data Facebook has on you to show you personalized ads.
Meta Platforms Inc., known formerly as Facebook, is a multinational tech group formed in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg. It is a parent company of several big social media nets including Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp. Meta is a publicly traded company, and its ownership is distributed among the shareholders. Ownership ratios can be changed due to stock transactions and market activities.
Some of Meta’s products include:
• Facebook, the social network platform, including the Facebook mobile app and in-app browser.
• Messenger app with instant message service, voice and video call capability.
• Instagram platform for visual content-complete with photos and videos.
• WhatsApp messaging client with its own voice and video call option.
• Oculus Virtual Reality platform with hardware (Rift, Quest) and a variety of VR experiences.
• Portal, a line of smart video communication devices for more intelligent video calls, equipped with AI-powered features.
• Workplace, the collaboration platform for teamwork, sharing and communication within any business.
The biggest concerns about Meta are user privacy, data security, rumors, speculation (i.e. the spread of disinformation or misinformation) and potential antitrust implications due to its market dominance.
How will users’ information be protected in this virtual environment? Their concern with Meta involves the privacy problem. Whether the company is capable of tackling this problem is open to question.
Meta Platforms earns most of its revenue by selling ads on social media platforms such as Facebook and Instagram. Meta’s advertising sales, focused on targeting such variables as age, sex, region, interests and habits, make for its main source of income. Moreover, the company sells a range of products and services in augmented and virtual reality — including hardware like the Meta Quest VR devices.
About the Facebook history timeline
Our timeline of Facebook’s history was created in PowerPoint using Office Timeline, a fast and intuitive tool designed to help users create eye-catching Gantt charts, timelines and roadmaps effortlessly. The visual is free to modify and share and can be edited or customized further either straight in PowerPoint, or using Office Timeline, which automates the whole process.
Download the Facebook history timeline for PowerPoint and get your free trial of Office Timeline to update it effortlessly or create your own beautiful visuals in minutes.
Tim is Co-Founder & CEO of Office Timeline, a Seattle-based start-up that aims to rid the world of boring, uninspiring meetings.
Turn project data into professional timelines
Get the advanced features of Office Timeline free for 14 days.